The Mer Wiki now uses your Mer user account and password (create account on https://bugs.merproject.org/)
Quality/Test processes
(→Package testing) |
(→Package testing) |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
# Get test results from the vendors | # Get test results from the vendors | ||
# Report OBS and build results back to gerrit | # Report OBS and build results back to gerrit | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Vendor qa process.png]] | ||
| + | |||
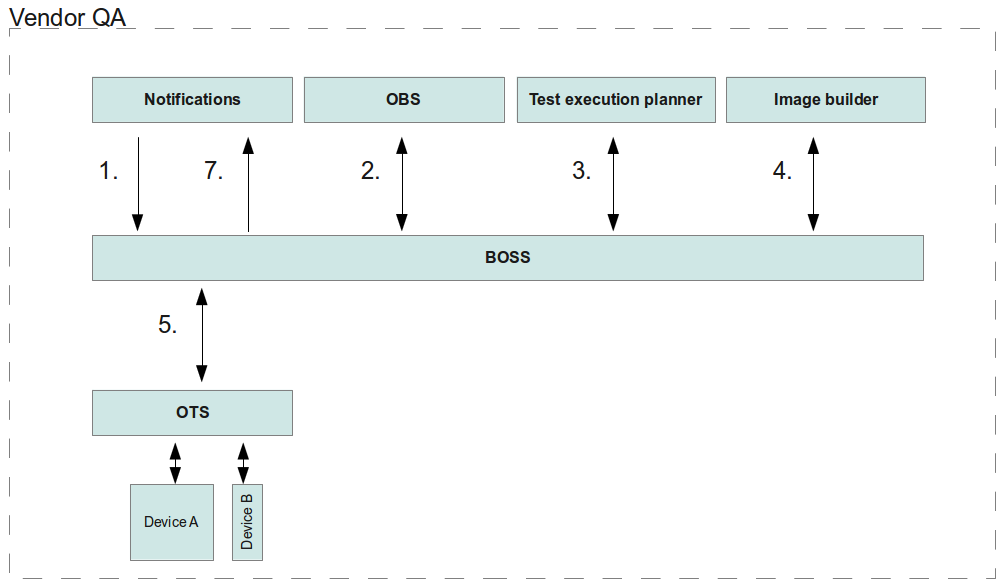
| + | # A vendor receives a test request notification from the Mer project | ||
| + | # The test request is delivered to the test execution planner | ||
| + | # The test execution planner creates kickstart files, lists needed packages for testing and test plans for the OTS | ||
| + | # The kickstart files and required package list is delivered to image builder | ||
| + | # Image builder creates testing images for all devices and returns image locations to BOSS | ||
| + | # Image locations and test plans are delivered to test automation, OTS | ||
| + | # After the test execution the test results are reported back to BOSS | ||
| + | # All results are delivered back to Mer QA | ||
=== Test mapping === | === Test mapping === | ||
Revision as of 07:02, 2 May 2012
Contents |
Mer QA process
Mer has two testing processes: package and release testing. Check the overall process description.
Package testing
Package test content should be fast to execute, no long lasting or soak tests, and should test the changed package thoroughly.
A contributor makes and submits a change which triggers the following process:
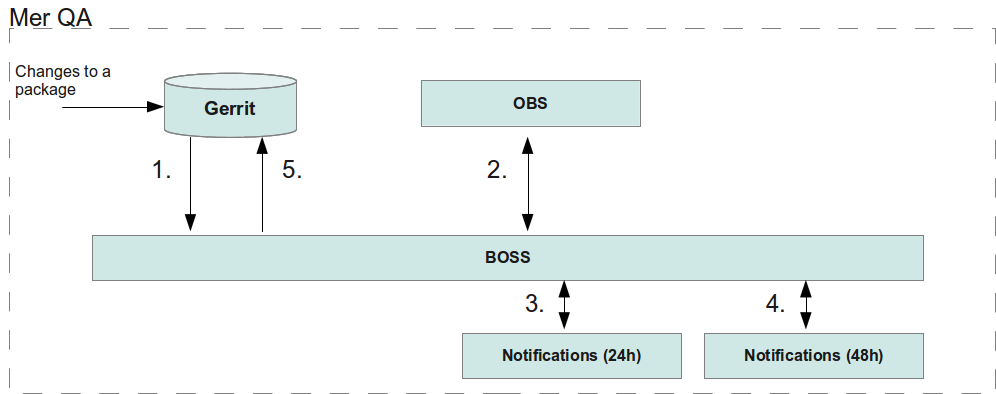
- BOSS notices the change in the gerrit
- BOSS delivers the changed package to OBS and OBS builds the package for all architectures
- The build result is reported back to BOSS
- If no errors in the building, send test request notification to vendors
- Get test results from the vendors
- Report OBS and build results back to gerrit
- A vendor receives a test request notification from the Mer project
- The test request is delivered to the test execution planner
- The test execution planner creates kickstart files, lists needed packages for testing and test plans for the OTS
- The kickstart files and required package list is delivered to image builder
- Image builder creates testing images for all devices and returns image locations to BOSS
- Image locations and test plans are delivered to test automation, OTS
- After the test execution the test results are reported back to BOSS
- All results are delivered back to Mer QA
Test mapping
One open issue with the package testing is that how to map tests to the package.
If all tests are using test packaging then the mapping could be like
<package name>:<test package name>[:tr-lite filter] bluez:bluez-tests bluez:blts-bluetooth-tests:testset=Core
- Another issue is then where the mapping is located and how it is defined. In XML file or database?
- If we want to keep it simple, then using text file and storing that in the git.
- Using similar principal than Mer project-core
- Text file can be JSON, YAML, XML
- Separated files for different testing processes/stages
- In Maemo, this information was in the Debian's control file.
- Defining relationship between the test packages
- ie given PkgA:TestA and PkgA:TestB when do you run TestA and when TestB?
- Extendable attributes, like "needs tcp, takes 4hours"
- Should these be in the test definition, not in the mapping?
- Possibility to define the test package version
- Example when testing new version of the package, only the new test package works with it
- Range of test package versions that can be used for testing or git SHA
Release testing
(Pre) Release testing has two main test sets: core and feature set. Both sets are executed to every release.
Release testing can take more time than package testing, and it should include non-functional tests.
Core set
The Core set contains set of tests that verify overall quality of the Mer Core release. It has tests for all architecture domains and API tests. Core set content is stable, only minor changes are allowed between the releases.
Feature set
Feature set includes tests for those packages that have changed from the previous release. Basically feature set is set of package testing tests. The feature set content changes to every release.
Manual testing
- QA Tools support manual testing.
- When manual tests can be executed and how to report results
- What is the testing process in manual testing
Reference QA processes
MeeGo
This is from the public side of the MeeGo!
- No CI testing in place
- Only hourly, nightly and release testing
- QA-Reports was used to report test results
- QA Tools were OTS, testrunner-lite, tdriver
- MCTS tests were used
Maemo
Please fix if you see mistakes here.
- Active CI testing in place
- Test packaging was used, the naming policy was strict
- Own dashboard for managing test packages
- Test package had in the Debian control file following parameters
- XB-Maemo-CI-Packages and XB-Maemo-CI-Stage
- When test package was updated to the version control, the control file information was moved to database
- When a package changed, tests that defined the package in the control file were executed
- Test packages were installed into the testing image and test automation executed all tests found from the image
- All tests from the test package were executed
- Caused problems if the test package had long or many test cases
- QA-tools were testrunner-lite, ots
- OTS had hundreds of test requests per day